Bluetooth
Enabling/disabling Bluetooth
Rfkill
Bluetooth can be disabled by using a software kill switch.
On some laptops, a hardware kill switch is also provided either via a special function key or key combination or a dedicated physical button or mechanism.
Using the rfkill command, you can see the state of these switches.
Open a terminal and type:
rfkill list
The output lists the state of software and hardware kill switches for all your wireless devices:
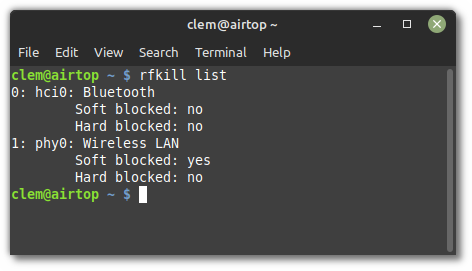
In the picture above you can see that Bluetooth is neither Soft blocked nor Hard blocked and is therefore enabled.
You can use rfkill to block (i.e. disable) or unblock (i.e. enable) bluetooth:
rfkill block bluetooth
rfkill unblock bluetooth
Blueman
Blueman is the default Bluetooth Manager in Linux Mint.
It provides the little Bluetooth icon in your system tray.
To disable Bluetooth right-click the tray icon and select Turn Bluetooth Off.
To enable Bluetooth right-click the tray icon and select Turn Bluetooth On.
To allow non-admin users on your system to disable or enable Bluetooth, they must be added to the netdev group.
You can do this with sudo adduser <username> netdev.
The very first time you open Blueman it asks if Bluetooth should be enabled automatically.
To check whether this feature is enabled open a terminal and type:
gsettings get org.blueman.plugins.powermanager auto-power-on
If auto-power-on is set to true, Blueman automatically unblocks Bluetooth at startup. Note that this setting is user-specific.
If you want to disable Bluetooth at startup you need to set auto-power-on to false:
gsettings set org.blueman.plugins.powermanager auto-power-on false
Note
The auto-power-on option was recently removed in Blueman’s master branch. It’s still present in Blueman 2.3.5 but it’s likely to disappear in newer versions.
Systemd-rfkill
Systemd provides a service which saves the state of your kill switches during shutdown and restores them on the next boot.
This service is a core part of systemd and is installed in Linux Mint by default.
Note
Blueman runs after systemd-rfkill, so if Blueman’s auto-power-on setting is enabled it overrides systemd-rfkill.
Bluez
Bluez is the Bluetooth stack used by Blueman.
Bluez has a setting called AutoEnable in the file /etc/bluetooth/main.conf.
If you don’t want Bluez to automatically enable Bluetooth during boot set this option to false.